Decoding the R2V R02V U1000 XLPE Cable Designation
Understanding the naming convention helps in selecting the right cable for your project:
- R2V/R02V: These designations often refer to European or IEC-standardized cable types (e.g., NF C 32-321), indicating a PVC-sheathed, fixed-installation power cable. While traditionally PVC-insulated, modern variants like the U1000 integrate XLPE for enhanced performance.
- U1000: Denotes a 1,000V voltage rating (0.6/1 kV), suitable for low-voltage power distribution in commercial and industrial settings.
- XLPE Insulation: Cross-linked polyethylene provides superior thermal resistance (up to 90°C), moisture resistance, and mechanical strength compared to standard PVC.
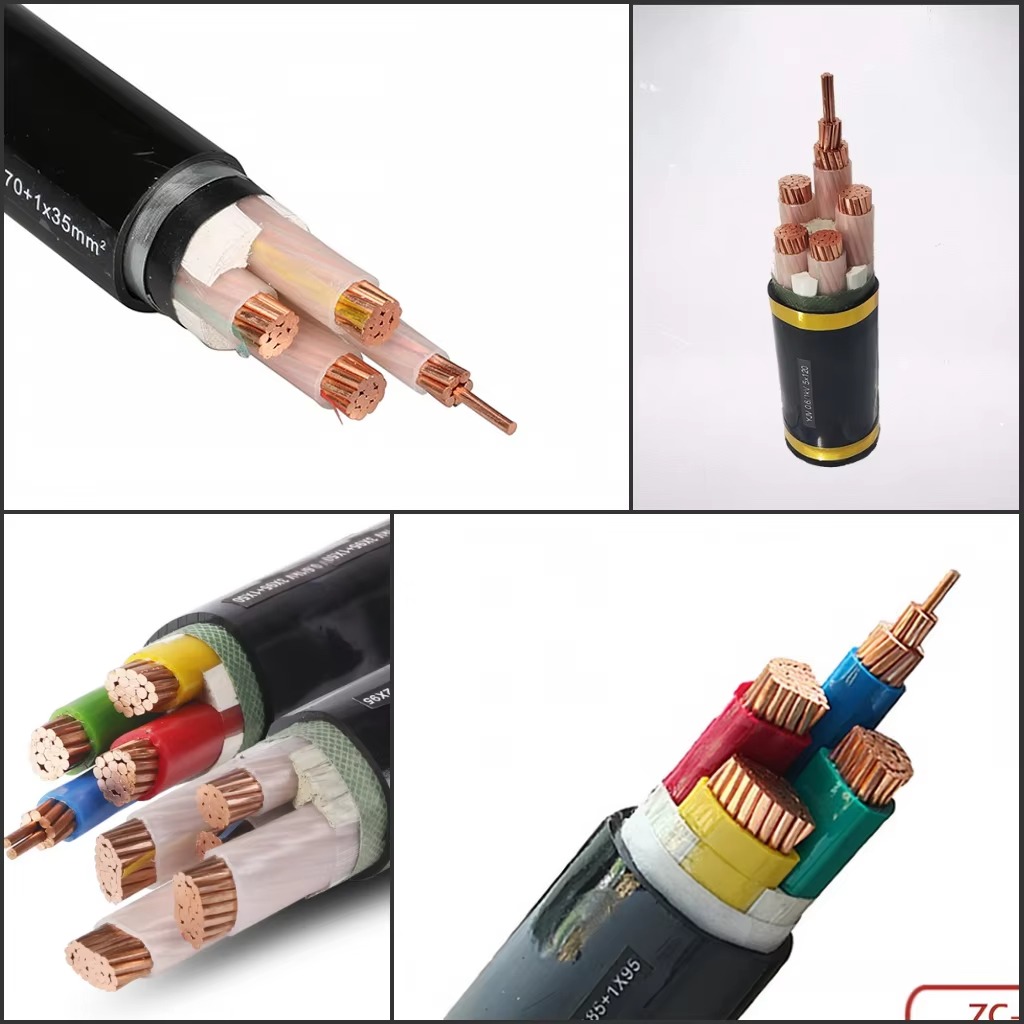

Technical Specifications & Compliance Standards
R2V R02V U1000 XLPE cables meet rigorous global standards, ensuring safety and interoperability:
- Voltage Rating: 0.6/1 kV (U1000)
- Conductor Material: Annealed copper (Class 2 stranded) or aluminum, offering high conductivity and flexibility.
- Insulation: XLPE (Cross-Linked Polyethylene) for thermal stability and chemical resistance.
- Sheath: Flame-retardant PVC or LSZH (Low Smoke Zero Halogen) options for fire safety.
- Temperature Range:
- Operating: -20°C to +90°C (short-term up to 250°C during faults).
- Installation: Minimum bending radius of 12x cable diameter.
- Standards Compliance: IEC 60502, BS 5467, VDE 0276, and RoHS/REACH directives.
Key Applications: Where These Cables Excel
The rugged design of R2V R02V U1000 XLPE cables makes them ideal for:
✅ Industrial Facilities: Powering machinery, control systems, and HVAC units in factories.
✅ Renewable Energy: Solar farms and wind turbines demand cables resistant to UV exposure and temperature swings.
✅ Infrastructure Projects: Underground/underwater installations, tunnels, and public transport networks.
✅ Commercial Buildings: Reliable power distribution in high-rise complexes, hospitals, and data centers.
Why XLPE Insulation Outperforms Traditional PVC
XLPE isn’t just a buzzword—it’s a game-changer for modern power cables:
- Higher Thermal Resistance: Withstands continuous operation at 90°C (vs. 70°C for PVC), reducing derating needs.
- Superior Durability: Resists abrasion, chemicals, and moisture, extending service life by 2–3x.
- Eco-Friendly: LSZH variants emit non-toxic fumes during fires, safeguarding lives and equipment.
- Cost-Effective: Lower maintenance and replacement costs over the cable’s 30+ year lifespan.
Installation Best Practices for Longevity
Maximize performance with these expert tips:
- Avoid Sharp Bends: Maintain a bending radius ≥12x the cable diameter to prevent insulation damage.
- Environmental Protection: Use conduit in corrosive or high-moisture areas (e.g., chemical plants).
- Load Management: Ensure proper derating in bundled installations to prevent overheating.
- Termination Kits: Use certified XLPE-compatible glands and joints to maintain insulation integrity.
FAQs: R2V R02V U1000 XLPE Cables
Q1: Is XLPE insulation better than PVC for underground cables?
A: Yes. XLPE’s moisture resistance and thermal stability make it ideal for buried installations, where PVC may degrade faster due to soil chemicals and temperature fluctuations.
Q2: Can R2V R02V U1000 cables be used in explosive environments?
A: Only if certified for ATEX/IECEx zones. Always verify flame-retardant (e.g., IEC 60332-1) or fire-resistant (IEC 60331) ratings for hazardous areas.
Q3: How does U1000 differ from U1000 R2V?
A: “U1000” refers to voltage rating (1 kV), while “R2V” specifies construction (e.g., PVC sheath). The combination denotes a 1 kV cable with R2V-style armor and XLPE insulation.
Q4: Are these cables recyclable?
A: XLPE itself is recyclable, but PVC sheathing complicates the process. Opt for LSZH-sheathed variants for easier end-of-life disposal.