What is BBTRZ Cable?
BBTRZ (Flexible Mineral Insulated Fire-Resistant Cable) represents a significant advancement in fire-resistant cable technology. Unlike traditional rigid mineral insulated cables, BBTRZ offers exceptional flexibility while maintaining impressive fire performance characteristics.
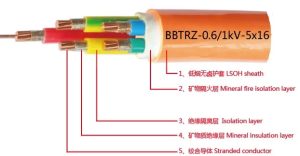
Technical Specifications of BBTRZ Cable:
- Full designation: Flexible fire-resistant copper sheathed inorganic mineral insulated cable
- Construction: Copper conductor, inorganic mineral insulation, longitudinally wrapped and welded copper tape sheath, and protective outer jacket
- Fire rating: Withstands 950°C flame temperature for 3 hours while maintaining circuit integrity at 1000V
- Flexibility: Can be manually bent on-site without special tools
- Environmental properties: Low-smoke, zero-halogen (LSZH) options available
- Applications: High-rise buildings, subways, hospitals, data centers, and other critical infrastructure
BBTRZ cables utilize advanced ceramic-forming compounds that transform into a solid ceramic insulation barrier when exposed to extreme heat, maintaining circuit integrity even in severe fire conditions.
Understanding YTTW Cable Technology
YTTW (also known as RTTZ in some markets) represents another approach to fire-resistant cable design. This cable type features a corrugated copper sheath construction that provides robust mechanical and fire protection.
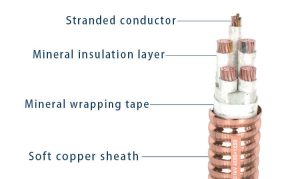
Technical Specifications of YTTW Cable:
- Full designation: Copper core, copper sheath, corrugated copper tape shielded, magnesium oxide insulated fire-resistant cable
- Construction: Copper conductor, compressed magnesium oxide insulation, corrugated copper sheath
- Operating temperature: Can function continuously at 250°C ambient temperature
- Fire rating: Maintains circuit integrity at 950°C for 180 minutes (meeting BS6387 C, W, Z tests)
- Flexibility: Semi-flexible but requires specialized bending tools for installation
- Applications: Power distribution in critical facilities, emergency systems, industrial plants
YTTW cables evolved from the rigid BTTZ mineral insulated cable technology but incorporated corrugation to improve flexibility while maintaining the excellent fire performance of mineral insulation.
Key Differences Between BBTRZ and YTTW Cables
1. Structural Composition
BBTRZ Cable Structure:
- No metal tube sheath (unlike traditional mineral insulated cables)
- Uses copper tape longitudinally wrapped and welded
- Outer PVC or LSZH protective jacket
- Mineral-based insulation compounds that ceramicize when exposed to heat
YTTW Cable Structure:
- Features a continuous corrugated copper sheath
- Uses compressed magnesium oxide as the primary insulation
- No separate outer jacket needed in many applications
- Mechanical protection comes from the metal sheath itself
2. Flexibility and Installation Characteristics
| Parameter | BBTRZ Cable | YTTW Cable |
|---|---|---|
| Bend radius | Can be bent by hand (≈6× cable diameter) | Requires specialized tools (≈12× cable diameter) |
| Installation speed | Faster installation with conventional tools | Slower installation requiring specialized equipment |
| Space requirements | Better suited for confined spaces and tight bends | Requires more space for routing and termination |
| Termination complexity | Standard termination techniques applicable | Specialized termination kits and training required |
3. Fire Performance Comparison
Both cables offer excellent fire resistance but with different performance profiles:
BBTRZ:
- Withstands 950°C for 3 hours while maintaining circuit integrity
- Low smoke emission during fire exposure
- Zero halogen options available for reduced toxicity
- No risk of sheath cracking under thermal cycling
YTTW:
- Withstands 950°C for 180 minutes (3 hours) per BS6387 standards
- Excellent water resistance during fire exposure
- Superior electromagnetic shielding properties
- Higher short-circuit current capability
4. Cost Analysis
Material Costs:
- BBTRZ: Lower material cost due to reduced copper content and PVC jacket
- YTTW: Higher material cost due to continuous copper sheath construction
Installation Costs:
- BBTRZ: Lower installation costs due to flexibility and standard termination methods
- YTTW: Higher installation costs requiring specialized tools and trained personnel
Lifecycle Considerations:
- BBTRZ: May require additional mechanical protection in harsh environments
- YTTW: Higher durability in mechanically demanding applications but requires moisture protection at terminations
Application-Specific Recommendations
When to Choose BBTRZ Cable:
- Projects with tight budget constraints where fire performance is still critical
- Installations requiring frequent bending or routing in confined spaces
- Applications where low smoke and zero halogen properties are mandated
- Retrofits and renovations where existing cable trays have limited space
When to Choose YTTW Cable:
- Critical infrastructure where maximum reliability is non-negotiable
- Environments with high electromagnetic interference requiring superior shielding
- Applications with extreme mechanical stress or rodent exposure concerns
- Projects with long service life requirements (50+ years) where initial cost is less critical than longevity
Expert Installation Tips
For BBTRZ installations:
- Ensure proper support spacing to prevent excessive sagging
- Use standard cable glands designed for the outer jacket material
- Maintain minimum bend radius during installation to avoid insulation damage
For YTTW installations:
- Use manufacturer-approved bending tools to prevent sheath damage
- Apply proper sealing compounds at all terminations to prevent moisture ingress
- Allow for thermal expansion in long vertical runs
- Ensure proper grounding of the copper sheath at both ends
Future Trends in Fire-Resistant Cables
The fire-resistant cable market continues to evolve with several emerging trends:
- Enhanced eco-friendly formulations: New BBTRZ variants with improved environmental profiles
- Hybrid designs: Combining the best features of both technologies
- Smart cables: Integration of monitoring capabilities to assess cable health
- Improved flexibility: Next-generation YTTW variants with better bending characteristics
- Higher temperature ratings: New insulation compounds pushing operational limits beyond current standards