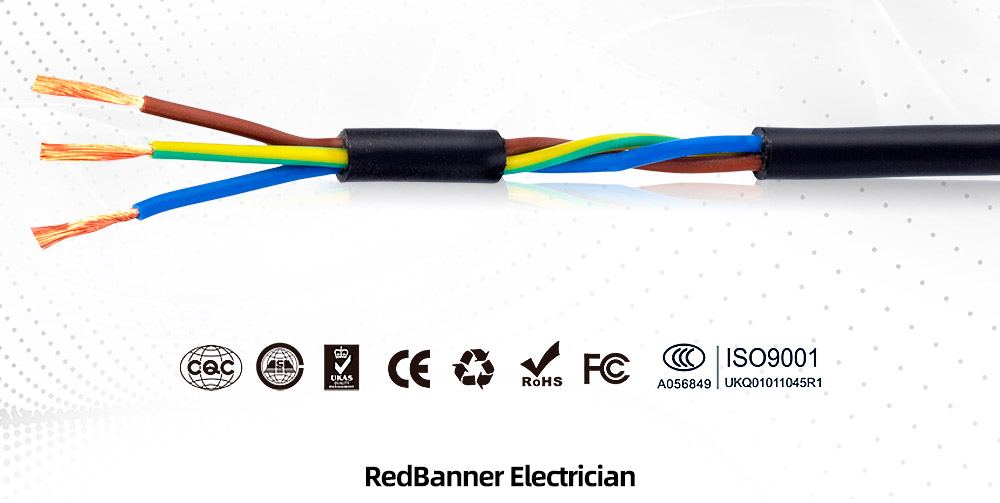
What Is RVV PVC Power Cable?
RVV PVC Power Cable is a flexible electrical cable with a full technical name: Copper Core Polyvinyl Chloride Insulated Polyvinyl Chloride Sheathed Flexible Cable. Often referred to as “soft sheathed wire” or “light PVC sheathed flexible wire,” RVV cable features multiple conductors surrounded by PVC insulation and an outer protective PVC sheath.
At its core, RVV cable consists of two or more RV wires (individual insulated conductors) bundled together within a common PVC protective sheath. This design provides excellent mechanical protection while maintaining good flexibility—making it ideal for applications requiring both durability and movement capability.
The name “RVV” itself reveals the cable’s composition:
- R = Flexible wire (soft conductor construction)
- V = PVC insulation material surrounding each conductor
- V = PVC outer sheath (the second V distinguishes it from single-insulated cables)
RVV Cable Construction Table
Understanding RVV cable construction helps in selecting the right cable for your specific application. Here’s a detailed breakdown of its layered structure:
| Layer | Material | Thickness | Function |
|---|---|---|---|
| Conductor | Multiple strands of annealed bare copper | Varies by gauge (0.5mm² to 6mm²) | Provides electrical conductivity with flexibility |
| Insulation | Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) | 0.6-0.8mm | Electrically isolates individual conductors |
| Filler | PVC compound or non-woven fabric | As needed | Maintains cable roundness and structural integrity |
| Outer Sheath | Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) | 0.8-1.2mm | Provides mechanical protection and environmental resistance |
The multi-stranded copper conductor ensures the cable remains flexible even after repeated bending, while the dual-layer PVC protection (insulation + sheath) creates a robust barrier against physical damage, moisture, chemicals, and electrical interference.
Applications of RVV PVC Power Cable
RVV cables find use across numerous industries and applications due to their versatility, safety features, and cost-effectiveness:
Residential Applications
- Power connections for household appliances (refrigerators, washing machines, air conditioners)
- Lighting circuits and fixture connections
- Home theater systems and entertainment centers
- Kitchen and bathroom electrical installations (resistant to moisture)
Commercial & Industrial Uses
- Control systems and signal transmission in automation equipment
- Security alarm systems and access control wiring
- Building intercom and communication systems
- Instrumentation and sensor connections
- Office equipment power supply cables
Specialized Applications
- Short-term outdoor temporary power (festivals, construction sites)
- Control panels and electrical cabinets
- HVAC system connections
- Retail display lighting and power systems
- Workshop and garage electrical installations
The cable’s flexibility makes it particularly valuable in tight spaces or where routing around obstacles is necessary. Its robust construction also ensures longevity in fixed installations where the cable might be exposed to mechanical stress or environmental factors.
Technical Characteristics of RVV PVC Power Cable
RVV cables are engineered to deliver reliable performance under various conditions. Key technical characteristics include:
- Voltage Rating: 300/300V or 300/500V (depending on specific variant)
- Temperature Range:
- Operating temperature: -15°C to +70°C
- Short-circuit temperature (max 5 seconds): +160°C
- Flexibility: Excellent bend radius (approximately 6× cable diameter)
- Flame Resistance: Self-extinguishing properties meeting IEC 60332-1 standards
- Chemical Resistance: Resistant to oils, acids, alkalis, and common solvents
- Moisture Protection: Low water absorption properties
- Electrical Properties:
- Conductor resistance meets IEC 60228 Class 5 requirements
- Insulation resistance >200 MΩ/km at 20°C
- Mechanical Strength:
- Tensile strength: ≥12.5 MPa
- Elongation at break: ≥150%
RVV cables typically carry CCC certification (China Compulsory Certification) and comply with international standards including IEC 60227 and GB/T 5023.5-2008.
RVV Cable Parameter Table
Selecting the right RVV cable requires understanding the available specifications. This table provides common configurations:
| Specification | Core Count | Conductor Area (mm²) | Approx. Outer Diameter (mm) | Max. Conductor Resistance (Ω/km) | Current Rating (A) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RVV 2×0.5 | 2 | 0.5 | 5.8 | 36.0 | 3 |
| RVV 2×0.75 | 2 | 0.75 | 6.2 | 24.5 | 6 |
| RVV 2×1.0 | 2 | 1.0 | 6.6 | 18.1 | 10 |
| RVV 2×1.5 | 2 | 1.5 | 7.5 | 12.1 | 15 |
| RVV 2×2.5 | 2 | 2.5 | 8.8 | 7.41 | 20 |
| RVV 3×1.5 | 3 | 1.5 | 8.2 | 12.1 | 15 |
| RVV 3×2.5 | 3 | 2.5 | 9.8 | 7.41 | 20 |
| RVV 4×1.5 | 4 | 1.5 | 9.0 | 12.1 | 15 |
| RVV 4×2.5 | 4 | 2.5 | 10.8 | 7.41 | 20 |
| RVV 5×1.5 | 5 | 1.5 | 10.0 | 12.1 | 15 |
Note: Values may vary slightly between manufacturers. Always consult specific product datasheets for precise specifications.
Available sheath colors typically include black, white, and gray, with black being the most common for general applications.
How RVV Differs from Other Cable Types
Understanding the distinctions between similar cable types ensures proper selection for your specific application:
RVV vs RV Cable
- RV Cable: Consists of only conductor + PVC insulation (no outer sheath)
- RVV Cable: Features conductor + PVC insulation + PVC outer sheath
- Key Difference: RVV provides superior mechanical protection and environmental resistance due to its outer sheath
- Application Impact: RV is better for frequently bent applications inside appliances; RVV is superior for fixed installations and harsher environments
RVV vs RVVP Cable
- RVV Cable: Has no shielding layer
- RVVP Cable: Includes an additional copper braid shielding layer between insulation and sheath
- Key Difference: RVVP offers electromagnetic interference (EMI) protection that standard RVV lacks
- Application Impact: RVVP is essential for sensitive signal transmission (audio equipment, data systems); RVV is sufficient for power applications without interference concerns
RVV vs VV Cable
- RVV Cable: Uses flexible stranded copper conductors
- VV Cable: Uses rigid single-strand copper conductors
- Key Difference: RVV is significantly more flexible and suitable for applications requiring movement
- Application Impact: VV cables are better for permanent fixed installations; RVV excels where flexibility during installation or operation is needed
Frequently Asked Questions About RVV PVC Power Cable
Q: Can RVV cable be used outdoors permanently?
A: Standard RVV cable is not designed for permanent outdoor installation. While it has some UV resistance, prolonged exposure to sunlight, rain, and temperature extremes will degrade the PVC sheath. For permanent outdoor applications, use specialized cables with UV-resistant and waterproof properties (often marked with “W” for weather-resistant).
Q: What’s the maximum operating temperature for RVV cable?
A: RVV cable can operate continuously at temperatures up to 70°C (158°F). This makes it suitable for most indoor applications but limits its use in extremely hot environments or high-load situations without proper derating.
Q: Is RVV cable suitable for underground burial?
A: No, standard RVV cable is not suitable for direct burial. Underground applications require cables with additional protection layers designed specifically for burial, such as armored cables (e.g., YJV22 or VV22 types).
Q: How does the flexibility of RVV compare to other common cables?
A: RVV is significantly more flexible than rigid cables like VV or YJV due to its stranded conductor construction. However, it’s slightly less flexible than RV cable (without sheath) because the outer sheath adds some stiffness. This balance makes RVV ideal for installations requiring moderate bending during setup but remaining fixed during operation.
Q: What’s the typical service life of RVV cable?
A: When properly installed within its specifications and environmental limits, RVV cable typically has a service life of 10-15 years. Factors that can reduce lifespan include exposure to extreme temperatures, continuous maximum load operation, mechanical stress, chemical exposure, and UV radiation.
Q: Can RVV cable be used for data transmission?
A: Standard RVV cable isn’t optimized for high-speed data transmission due to lack of shielding and specific impedance characteristics. For data applications, use specialized cables like RVVP (shielded version) or dedicated data/communication cables (Cat5e, Cat6, etc.) designed for signal integrity.