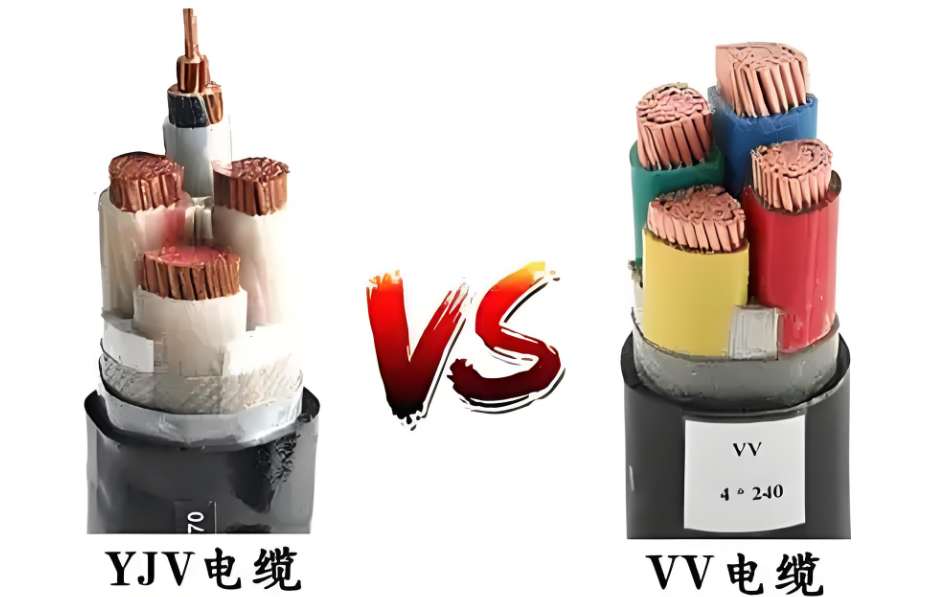
In electrical engineering and construction projects, choosing the appropriate power cable type directly impacts system reliability, safety, and long-term operational costs. Among the most commonly used power cables globally, YJV and VV cables represent two distinct technologies with significant performance differences. While many contractors and electricians still debate which option offers better value, understanding their technical specifications is crucial for optimal selection.
What Are YJV Cables?
YJV (Cross-linked Polyethylene Insulated PVC Sheathed Power Cable) represents modern cable technology with enhanced performance characteristics. The designation “YJV” breaks down as follows:
- YJ: Cross-linked polyethylene (XLPE) insulation
- V: PVC sheath/outer covering
Technical Specifications of YJV Cables
- Maximum operating temperature: 90°C (significantly higher than VV cables)
- Short-circuit temperature tolerance: Up to 250°C (for maximum 5 seconds)
- Installation temperature requirements: Not below 0°C
- Manufacturing standards: GB12706, IEC60502-2:2005, GB/T10438-2004
- Voltage range: Typically 0.6/1kV to 35kV
The cross-linked molecular structure of XLPE insulation gives YJV cables superior electrical properties, making them suitable for demanding applications where performance and longevity are priorities.
What Are VV Cables?
VV cables (PVC Insulated and Sheathed Power Cable) represent conventional cable technology that has been widely used for decades. The designation “VV” indicates:
- First V: PVC insulation
- Second V: PVC sheath/outer covering
Technical Specifications of VV Cables
- Maximum operating temperature: Typically 70°C
- Material composition: Standard polyvinyl chloride for both insulation and sheathing
- Cost profile: Generally 15-25% less expensive than comparable YJV cables
- Voltage applications: Primarily low voltage applications
While VV cables remain in use due to their affordability, industry trends show a gradual shift toward YJV technology for most new installations.
Key Differences Between YJV and VV Cables
1. Insulation Material and Technology
YJV cables utilize cross-linked polyethylene (XLPE), which undergoes a chemical process that creates stronger molecular bonds. This cross-linking dramatically improves thermal stability and electrical properties. VV cables use standard PVC insulation without this enhancement process, resulting in more limited performance characteristics.
2. Temperature Resistance
This represents one of the most significant differences:
- YJV cables maintain integrity at continuous operating temperatures up to 90°C
- VV cables are typically rated for maximum continuous operation at 70°C
This 20°C difference substantially impacts current-carrying capacity and safety margins, particularly in high-load applications or environments with ambient heat.
3. Electrical Performance
YJV cables demonstrate superior:
- Dielectric strength
- Insulation resistance
- Current-carrying capacity (typically 15-20% higher than equivalent VV cables)
- Performance stability over time
4. Service Life Expectancy
Due to the enhanced thermal properties and resistance to environmental factors:
- YJV cables typically offer 30+ years of service life under proper conditions
- VV cables generally provide 15-20 years of service life
5. Cost Considerations
- YJV cables command a 15-25% price premium over comparable VV cables
- However, their longer service life and higher performance often result in better value over the cable’s lifetime
- Maintenance and replacement costs must factor into total cost of ownership calculations
Comparative Application Guide
When to Choose YJV Cables
- High-temperature environments (industrial facilities, power plants)
- Applications requiring maximum current capacity
- Critical infrastructure where reliability is paramount
- Underground installations with limited cooling
- Projects with extended design life requirements
- Applications subject to frequent load fluctuations
When VV Cables May Be Suitable
- Budget-constrained projects with standard requirements
- Temporary installations with limited service life
- Low-load applications in temperature-controlled environments
- Short-distance internal wiring where heat buildup is minimal
- Applications where replacement access is easy and cost-effective
Performance Comparison Table
| Characteristic | YJV Cables | VV Cables |
|---|---|---|
| Insulation Material | Cross-linked Polyethylene (XLPE) | Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) |
| Max Operating Temperature | 90°C | 70°C |
| Short Circuit Temperature | 250°C (max 5 seconds) | ~160°C |
| Typical Service Life | 30+ years | 15-20 years |
| Current Carrying Capacity | Higher (baseline 100%) | 15-20% lower |
| Cost Factor | 1.0 (baseline) | 0.75-0.85 |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent | Moderate |
| Moisture Resistance | Excellent | Good |
| Applications | High-performance, critical systems | Standard, budget-sensitive projects |
Industry Trends and Future Outlook
The global cable market is witnessing a steady transition from VV to YJV technology. According to industry reports, YJV cable adoption has grown approximately 8% annually over the past five years, while VV cable usage has declined correspondingly. This shift reflects increasing emphasis on:
- Energy efficiency requirements
- Longer infrastructure lifespans
- Reduced maintenance costs
- Enhanced safety standards
In many regions, electrical codes and standards are increasingly specifying XLPE-insulated cables like YJV for new construction, particularly for commercial and industrial applications.
Expert Selection Tips
- Calculate total cost of ownership: While YJV cables cost more initially, their extended service life often makes them more economical over time.
- Consider installation environment: High ambient temperatures, direct sunlight exposure, or proximity to heat-generating equipment favor YJV’s superior thermal performance.
- Evaluate load profiles: Applications with consistent heavy loads benefit significantly from YJV’s higher temperature rating.
- Assess accessibility for replacement: In difficult-to-access installations, the longer lifespan of YJV cables represents significant value.
- Check local regulations: Building codes increasingly mandate higher-performance cable types for certain applications.